When you see a solid roof from corrugated board, you do not think about what it rests on? How complex is the design that serves as the basis for the gofrolist? Decking - a simple and lightweight material for self-laying on the roof. It is easy to assemble a crate for it, having the usual construction tool and some skills to work with it.
Content
The device of a wooden lathing under a professional flooring
For working with corrugated board, the most successful version of the roof structure is gable or gable broken. It does not have to cut corners, and often you can do without cutting corrugators. It’s a little harder to work with a hip roof. It is better to cover architectural objects of complex geometry not with sheet, but with ordinary material.
Profiled sheet - light coating. Therefore, if it is not planned to equip the residential attic in the under-roof space, you can use rafter beams of 100x150 or 100x200 mm. The pitch between the rafters is set 60–90 cm.
The choice of crate depends on the slope of the roof and the grade of corrugated board. The minimum allowable angle for the roof corrugated sheet is 12 °. At 12-15 ° and using corrugated sheets of grades S-10 and C-20, they make a continuous crate of moisture-resistant plywood 12 mm or 9 mm OSB-3.

For a larger slope and a relief profile, a sparse crate is installed. The higher the corrugation of the corrugated board and the angle of inclination of the roof, the less often the board is stuffed. Stamps of supporting corrugated board can be laid on a roof of 8-11 ° on a sparse crate.

Metal crate
Sometimes, for the installation of a corrugated sheet roof, a metal crate is used. As a rule, these are industrial and technical buildings covered with 0.7 mm metal. Their roofs are made with a small angle or flat.
The metal profile is screwed to the rafters with screws or bolts. And if the rafters are made of pipe, corner, channel, then they are welded. The entire structure must be treated with anti-corrosion enamel or primer.
The need for waterproofing
The main enemy of wooden and metal roofing structures is condensate. It is formed from steam rising from heated rooms. Drops of water often hang on the bottom of the coating in the morning, when the corrugated sheet is heated by the sun and the air temperature below it reaches the dew point. High-quality corrugated board is covered with a layer of non-wettable polymer paint. But moisture can seep into the mounting holes, lathing wood, insulation.
Insulated attic
The roofing structure is insulated by laying mineral wool between the rafters. With ascending flows of warm air, steam passes through the pores of the insulation and rises above.
For insulated roofs, an anti-condensation waterproofing film is used. This is a three- or four-layer rolled polymer material that absorbs ascending steam, but does not let it pass under the roof. The accumulated moisture is gradually removed to the sides through the edges of the waterproofing. The anti-condensation film is mounted with a double-sided ventilation gap:
- the insulation is laid 2-3 cm below the upper level of the rafters,
- the film is stretched and fixed on the rafters,
- a counter-lattice of 20–50 mm rails is filled,
- the crate is stuffed.

Uninsulated attic
Membranes are good in that they retain water, but let steam in both directions and do not create a greenhouse effect. But when using them, it is necessary to create a ventilation gap:
- the membrane is stretched on the rafters,
- the crate is stuffed,
- the crate is stuffed.

Installation materials and tools
In low-rise housing, the rafter system and crate are constructed of wood. This material does not overload the load-bearing elements, it is strong enough and has low thermal conductivity. For sparse crates, a bar of 50x50 mm, 50x100 mm, an edged board of 20x100 mm is used. The best wood is spruce and pine. It is cheap, but it lasts long enough due to its natural resistance to moisture and insect attacks. Nevertheless, the finished crate for reliability should be treated with an antiseptic.
In addition to lumber, you will need:
- nails or self-tapping screws 80-100 mm,
- hammer,
- drill,
- screwdriver or screwdriver,
- jigsaw or hacksaw,
- roulette,
- level,
- cord.
The work will be greatly facilitated by the band sawmill.
Roofing works belong to the category of high-rise ones, therefore compliance with safety measures - mounting belts, insurance slings, protective clothing, protective equipment - is a prerequisite for their implementation. Do not do roofing in strong winds.

Calculation of the required amount of lumber
For continuous
Calculating the required amount of OSP-3 or plywood for a continuous crate is easy. Use the design documentation for the house:
- calculate the total roof area,
- multiply the length of the eaves by the length of the eaves overhang of 40-100 cm,
- multiply the height of both slopes by the length of the front overhang.
Adding the three numbers obtained, you calculate the total area of the sheet material for a continuous crate. Add 5% to inevitable waste.
For sparse
The amount of timber for a sparse crate is calculated according to the table.
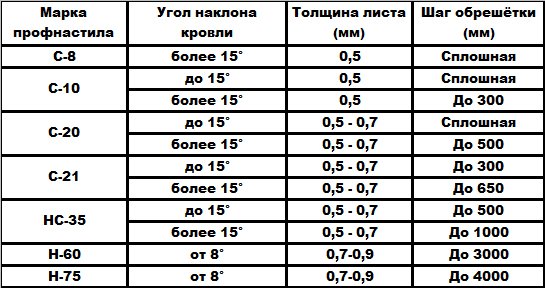
- Calculate how many rows will be laid on the rafters - divide the height of the slope by the step of the crate.
- Add two additional rows to the cornice board, two rows to the ridge board.
- Multiply the resulting number by the length of the cornice.
- Add a perimeter around the chimney, ventilation shaft, fire hatch, etc.
- Add 10% to the waste that is unavoidable when cutting lumber.
Installation procedure
Install the crate should be three or four. At least 2 people must lay and fasten the boards. And at least one must supply lumber, supplies, tools from zero.
- Mark the outer rafters. Check the horizontal direction with a level, determine the straightness of the marking with a cord.
- Fix the cornice and ridge boards with self-tapping screws or nails. Drive 2 fasteners at each intersection of the board with the rafter. Savings in the fastening material will eventually lead to deformation of the roof covering.
- Nail the reinforcing boards around the roof exits.
- Laying boards of the main crate begin from the ridge. The butt joints of the ends should be in the middle of the rafter. In the subsequent rows, the joints move to the other legs of the rafters.
- Fill the front board onto the front cornices. It should have a height equal to the height of the corrugation of the corrugated board.
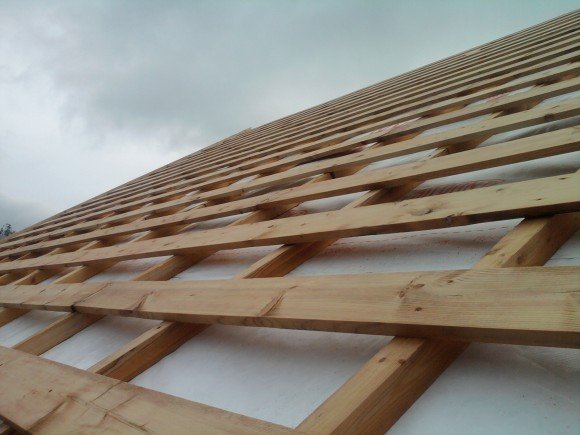
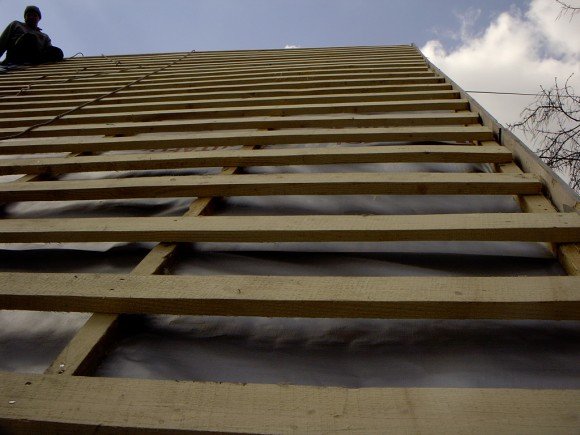


The installation of the crate is carried out in dry, calm weather. Timber that gets wet in the rain during subsequent drying may become deformed or crack.
Installation of the crate under the corrugated board is one of the simplest stages of roofing work. The necessary tools for its implementation are available in the arsenal of any home master. If you like to create coziness on your own and know how to be proud of the work of your own hands, you will certainly cope with this task!
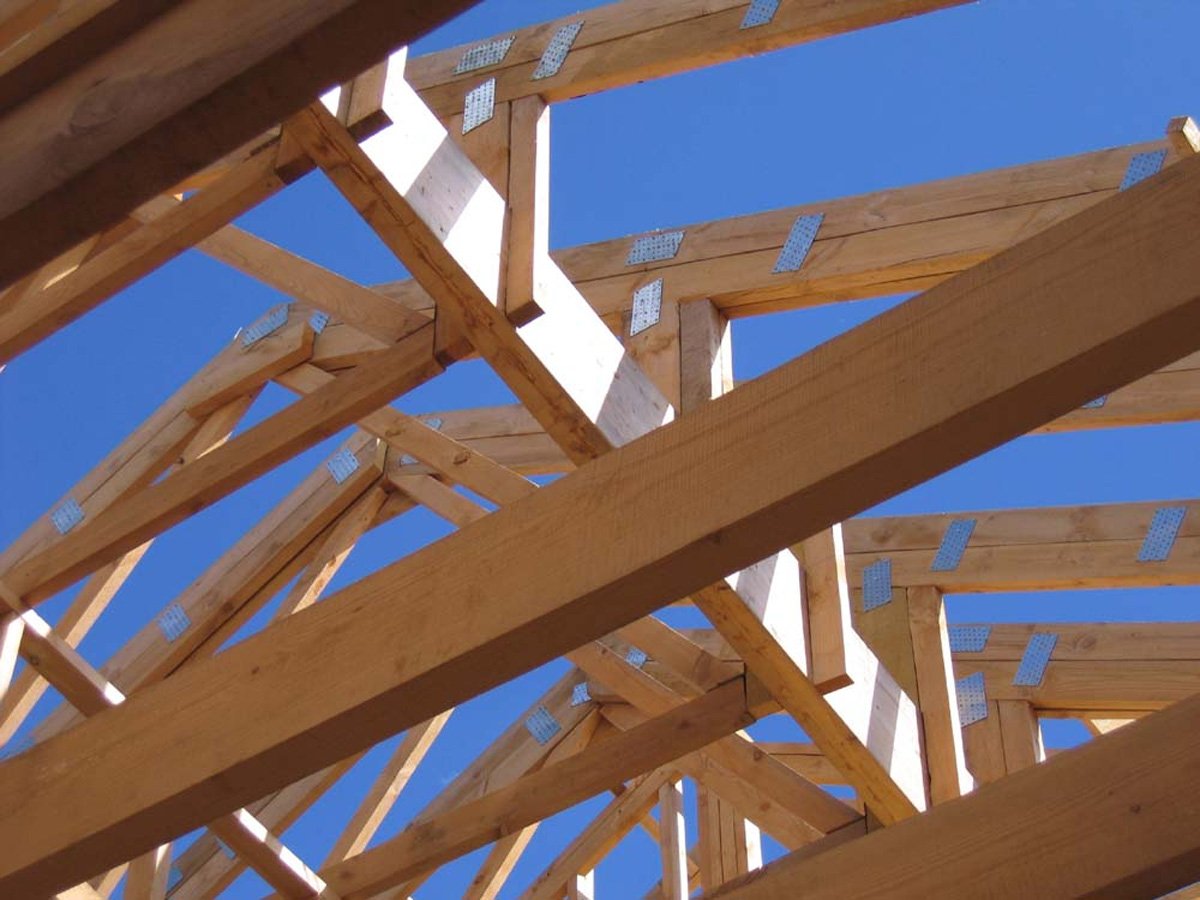





Alas, no comments yet. Be the first!