Modern science distinguishes between such concepts as weight and mass. This occurs primarily because weight is a force characteristic, i.e. a measure of the impact on the support or suspension. Mass, on the contrary, is a measure of the inertia of the body. We write all this so that during the reading of this article you do not have questions about how the weight of the channel and its mass differ. For simplicity, we consider only those situations where these two parameters are equivalent.
In the case of profiles, the mass depends on the following parameters:
- Forms
- Metal;
- Sizes.
Shape and size
Speaking about the form, it is necessary to clarify that profiles are of several types, for example, classic and perforated.

Metal structures can be made not only of steel, so when it comes to other alloys, this will be indicated separately. We are clarifying this moment, since the weight of the channel 12 made of aluminum will be several times lower than in the case when steel is used.
In the usual case, the mass of the profile is calculated quite simply, but only if its shape is simple. Those. we consider an equal-shelf product, the inner faces of the walls of which are parallel to each other. There are also unequal profiles for which the calculation of mass is somewhat complicated, but the most difficult option is the inclined faces of the inner walls. Such a product is very massive, but this is offset by increased strength, due to the large volume of metal.
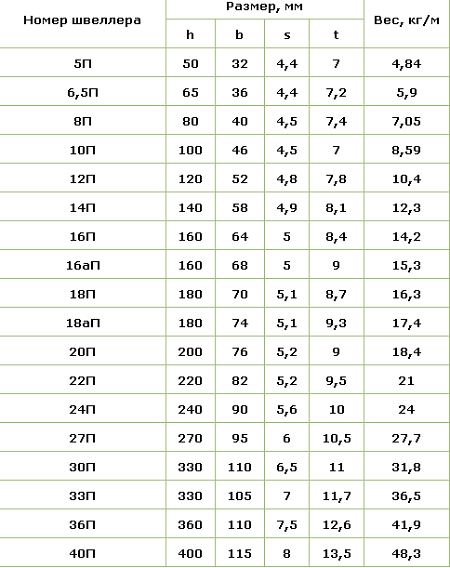
The weight of the channel 10 can vary from 3 to 12.7 kg, depending on its dimensions. In this case, such a large spread is provided due to different wall heights. It starts from a mark of 40 mm and can reach 160 mm, due to which a very deep profile is formed. The thickness also does not remain constant and varies from 2 to 6 mm.
If we consider all the numbers of the bent profile, then we can say that the channel with the ratio h: b: s 25: 26: 2 mm has a minimum mass. The weight of such a profile barely exceeds 1 kg. On the other side of the size line is number 41, which can be represented in the form of a similar ratio of 410: 65: 6 mm and the weight of only one meter will be 24.38 kg.

A higher channel number does not mean that this product will be heavier. The weight of the channel 20 will be less than that of number 21, only if the dimensions of the walls and the thickness of the product are the same, otherwise even No. 20 will be able to bypass 21 profiles.
The mass of hot-rolled profiles starts from 4.84 kg for a 5U product, the dimensions of which can be represented as 50: 32: 4.4 mm and a length of 1 m. With a wall height of 40 mm and an inclination of the inner edges, a weight of 48.3 kg per 1 m is obtained This is due to the fact that the metal consumption for such a channel is very large, and its dimensions are 400: 115: 8 mm.
Metal
Usually, when talking about the tabular value of the mass or weight of profiles, examples of which we gave in the previous paragraph, they mean some abstract steel with a density of 7.85 units and a product length of 1 m. In reality, the situation is somewhat different, since the most different alloys.
One of the interesting options for various unloaded designs is aluminum. This is a fairly common silver-white metal today, whose density is 2.7 units. Obviously, the weight of the channel 14 from such a material will be much lighter than steel; another thing is that creating such large structures from aluminum is not always advisable.

As a structural material, aluminum is very attractive not only for its low weight, but also for being easily stamped, and also does not require any additional protection. Of course, during the manufacturing process, the production of profiles from this metal is accompanied by various procedures that allow to slightly increase the strength of the product.

On the other hand, steel is used even more often than aluminum, and the most common options are its carbon and low alloy varieties. The quality of carbon steels is determined by the presence of impurities in them. The most dangerous are sulfur and phosphorus. Due to sulfur, the red-brittleness of the metal occurs, and because of phosphorus, brittleness occurs. For ordinary steel, these components cannot exceed 0.05%. Within such a group, the mass of 1 m3 changes insignificantly; therefore, the influence of impurities on the weight of the channel can be neglected. In this case, the metal marking is "St". A higher-quality variety already has the designation "Steel", and the content of S and P is less than 0.035%. There are two more varieties of such alloys of high quality and special quality, in which the proportion of harmful impurities is less than 0.025% and 0.015%, respectively. For high-quality steel, marking “A” at the end of the grade is used, and for higher quality “Sh”.

The type of steel affects the mass of a meter profile. For example, the weight of the channel 16 made of carbon steel will be different from the result obtained using a alloy alloy.
Alloy steel is an alloy that, in addition to basic impurities, contains a number of elements that are introduced in certain quantities. These are alloying additives for which chromium, copper, bound nitrogen, nickel or vanadium are chosen. All alloy steels are divided into 3 categories:
- low alloyed;
- medium alloyed;
- highly alloyed.
In the first case, we are talking only about 2.5% of impurities, in the second they can be up to 10%, and highly alloyed compounds often have 50% of impurities.
Summing up, we note that we examined most of the factors affecting the weight of the channel. It should also be noted that when weighing a batch, it will be necessary to take into account small deviations caused by various errors, which is clearly stated in the relevant state standard.





Alas, no comments yet. Be the first!